Introduction
In the realm of digital security, the term “Antimalware Service Executable” often raises questions and sometimes concerns among Windows users. This vital component of Windows Defender ensures your computer stays protected from malicious threats. However, many users report that it consumes a significant amount of system resources, leading to performance issues. This comprehensive guide will delve into what the Antimalware Service Executable is, why it might be affecting your PC’s performance, and how to manage it effectively.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, is a core process of Windows Defender, Microsoft’s built-in antivirus solution. It runs in the background, constantly monitoring your system for potential threats such as viruses, spyware, and other malicious software. This process is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of your computer.
The Role of Antimalware Service Executable
Antimalware Service Executable performs several essential functions:
1. Real-Time Protection: Continuously scans files, applications, and downloads to detect and block threats before they can harm your system.
2. Full System Scans: Periodically performs comprehensive scans of your entire system to ensure no threats are lurking undetected.
3. Threat Remediation: Removes or quarantines detected threats to prevent them from causing damage.
These functions are critical for keeping your system secure, but they can also be resource-intensive, which sometimes leads to performance issues.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Use High CPU?
Many users have reported that the Antimalware Service Executable consumes a large amount of CPU and memory resources, leading to slower system performance. There are several reasons for this:
1. Full System Scans: During full system scans, the Antimalware Service Executable will naturally use more resources as it thoroughly checks all files and applications.
2. Real-Time Protection: Constantly monitoring your system for threats requires significant processing power, especially if you’re running resource-heavy applications simultaneously.
3. Software Conflicts: Sometimes, other software or malware can conflict with Windows Defender, causing the Antimalware Service Executable to work harder and use more resources.
Understanding these factors can help you manage the impact on your system’s performance.
How to Check Antimalware Service Executable Resource Usage
Before taking any steps to address high resource usage, it’s essential to verify that the Antimalware Service Executable is the cause. Here’s how you can check its resource usage:
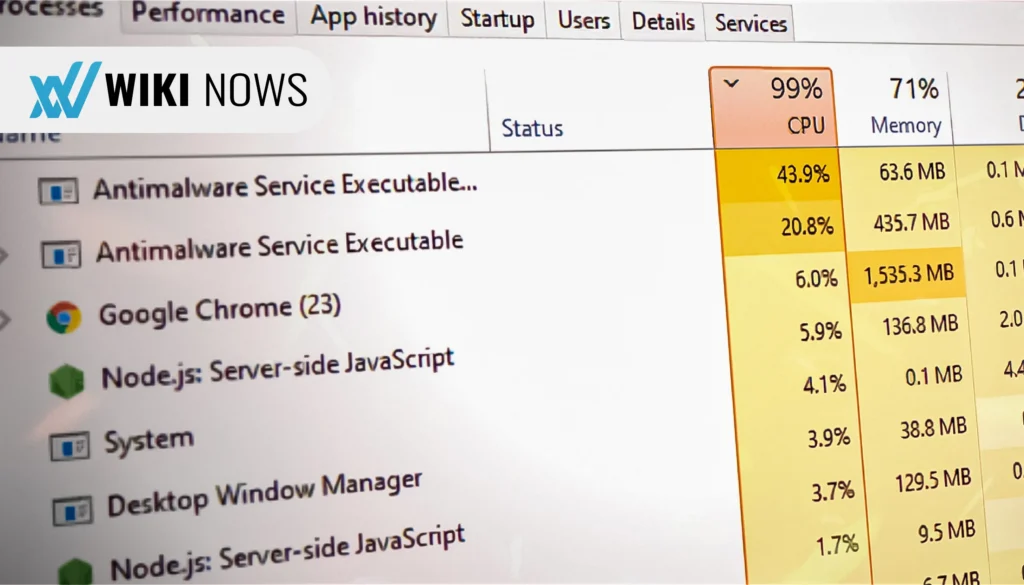
1. Open Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager.
2. Navigate to Processes Tab: In the Task Manager window, click on the Processes tab.
3. Locate Antimalware Service Executable: Scroll down and look for Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe.
4. Check CPU and Memory Usage: Observe the percentage of CPU and memory being used by this process.
If you notice that the Antimalware Service Executable is consistently using a high amount of resources, it’s time to take action.
Managing Antimalware Service Executable for Better Performance
There are several strategies you can employ to manage the resource usage of the Antimalware Service Executable without compromising your system’s security:
1. Schedule Scans During Downtime
Scheduling full system scans during periods when you’re not actively using your computer can help minimize the impact on performance. Here’s how to do it:
- Open Windows Security from the Start menu.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click on Manage settings under Virus & Threat Protection settings.
- Scroll down and click Add or Remove exclusions.
- Add files, folders, or processes that you want to exclude from scans.
2. Adjust Windows Defender Settings
Tweaking certain settings in Windows Defender can also help reduce the resource usage of the Antimalware Service Executable:
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click Virus & Threat Protection settings.
- Turn off Real-time protection temporarily if you’re running resource-heavy applications (remember to turn it back on afterward).
3. Optimize Your System
General system optimization can also alleviate performance issues caused by the Antimalware Service Executable:
- Update Windows: Ensure your operating system and all software are up to date.
- Clean Up Your System: Remove unnecessary files and applications.
- Increase RAM: Adding more memory can help your system handle resource-intensive processes more efficiently.
Advanced Solutions for High CPU Usage
If basic adjustments don’t resolve the issue, you can try more advanced solutions:
1. Disable Scheduled Tasks
Disabling specific Windows Defender tasks can reduce the frequency of resource-intensive scans:
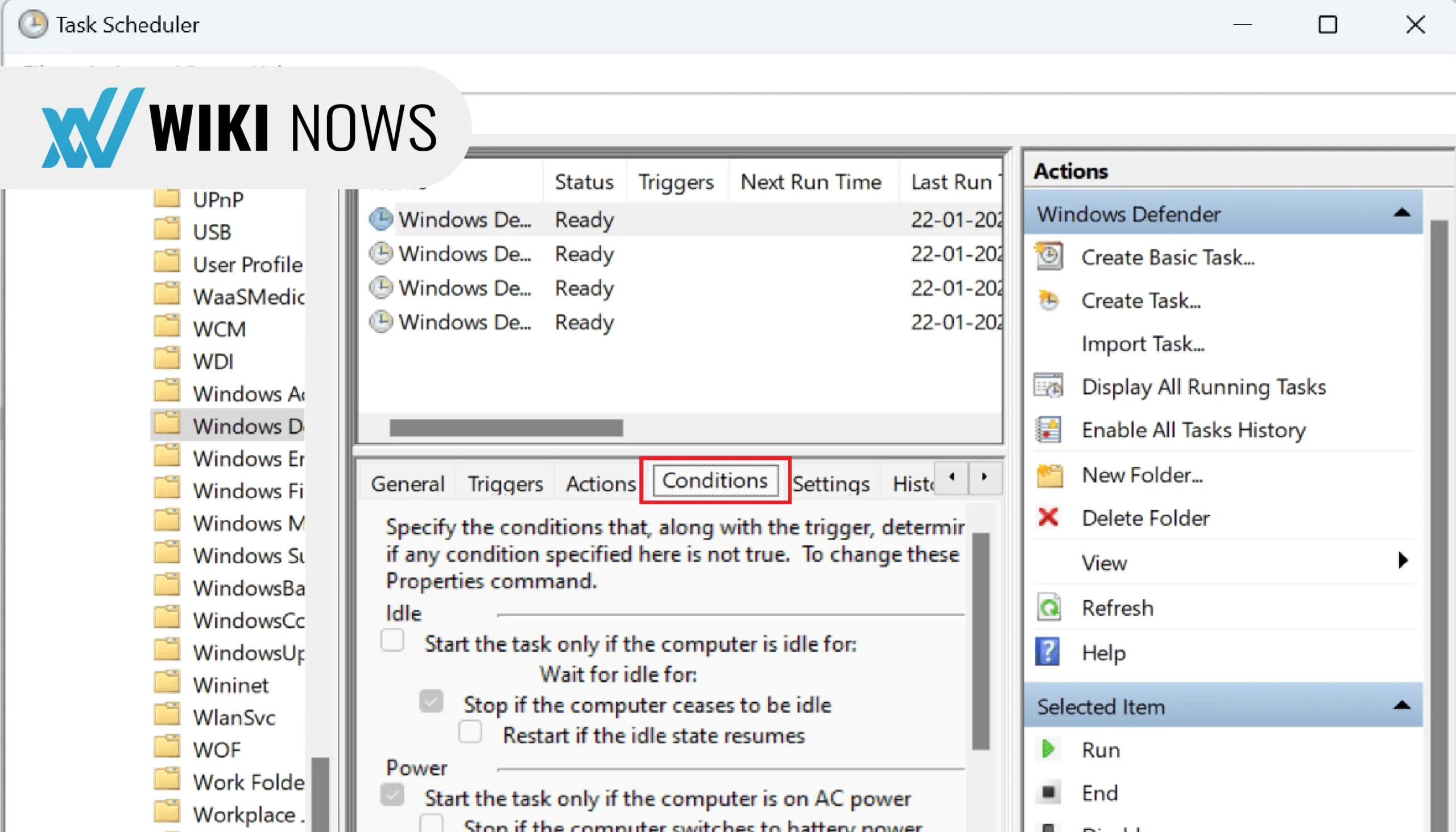
- Open Task Scheduler from the Start menu.
- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
- Disable the tasks named Windows Defender Scheduled Scan, Windows Defender Cache Maintenance, Windows Defender Cleanup, and Windows Defender Verification.
2. Third-Party Antivirus Software
Switching to a third-party antivirus solution can also help if Windows Defender is causing persistent performance issues. Ensure you choose a reputable antivirus that offers robust protection without high resource usage.
Understanding Exclusions in Windows Defender
Excluding specific files, folders, or processes from Windows Defender scans can reduce the workload of the Antimalware Service Executable. Here’s how to add exclusions:
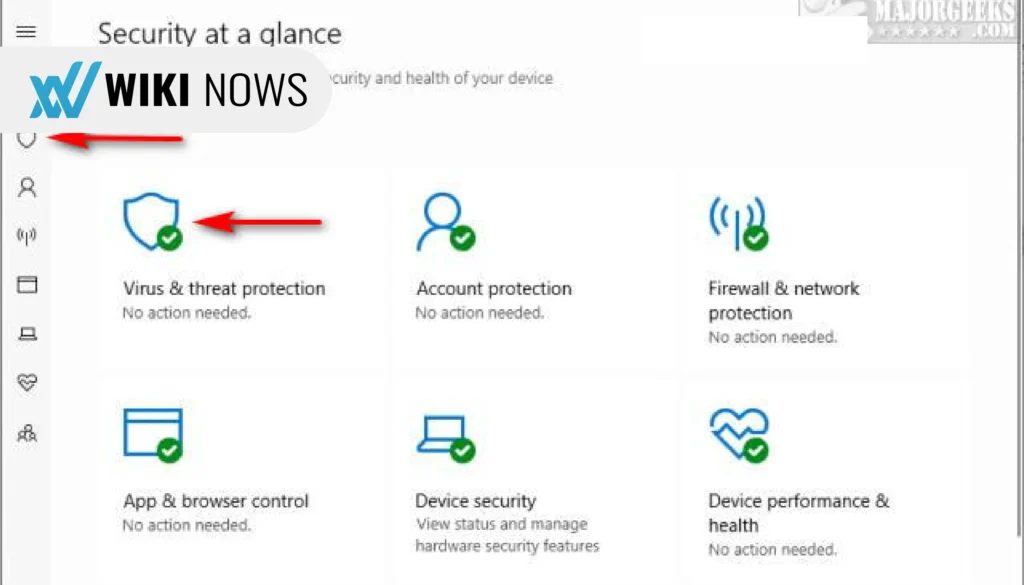
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click Manage Settings under Virus & Threat Protection settings.
- Scroll down and click Add or Remove exclusions.
- Add the files, folders, or processes you want to exclude from scans.
Be cautious with exclusions, as they can potentially expose your system to threats if misused.
Balancing Security and Performance
Striking the right balance between security and performance is crucial. While it’s important to manage the resource usage of the Antimalware Service Executable, never compromise your system’s protection. Regularly update your antivirus software, avoid downloading files from untrusted sources, and maintain good cybersecurity practices.
Common Myths About Antimalware Service Executable
There are several misconceptions about the Antimalware Service Executable that can lead to confusion:
1. Myth: Disabling Windows Defender Improves Performance Significantly
While disabling Windows Defender might temporarily reduce CPU usage, it leaves your system vulnerable to threats. Instead of disabling it, consider optimizing its settings as described above.
2. Myth: Antimalware Service Executable is Unnecessary
Some users believe they don’t need the Antimalware Service Executable because they have other security measures in place. However, it’s a critical component of Windows Defender, providing essential protection against malware.
3. Myth: High Resource Usage Means Inefficiency
High resource usage during scans doesn’t necessarily mean the Antimalware Service Executable is inefficient. It’s performing a thorough check of your system, which is resource-intensive by nature.
Best Practices for Maintaining System Performance
To keep your system running smoothly while ensuring robust security, follow these best practices:

1. Regularly Update Software: Keep your operating system, antivirus, and all other software up to date to benefit from the latest performance improvements and security patches.
2. Perform Regular Maintenance: Clean up unnecessary files, uninstall unused applications, and defragment your hard drive if necessary.
3. Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly check the Task Manager to identify processes that may be consuming excessive resources.
4. Use a Lightweight Antivirus: If Windows Defender continues to cause performance issues, consider using a lightweight third-party antivirus solution.
Conclusion
The Antimalware Service Executable is an essential part of your system’s defense against malware and other threats. While it can sometimes cause high CPU and memory usage, there are several strategies you can employ to manage its impact on your system’s performance. By scheduling scans during downtime, adjusting Windows Defender settings, optimizing your system, and considering advanced solutions, you can maintain a secure and efficient computer environment. Remember, the goal is to balance security and performance, ensuring your system remains protected without sacrificing usability.
Understanding the intricacies of the Antimalware Service Executable empowers you to take control of your system’s performance and security, providing peace of mind in an increasingly digital world. Keep your defenses strong and your system optimized to enjoy a seamless computing experience.